Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Features
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
Startup Failure Rate Statistics (2025)
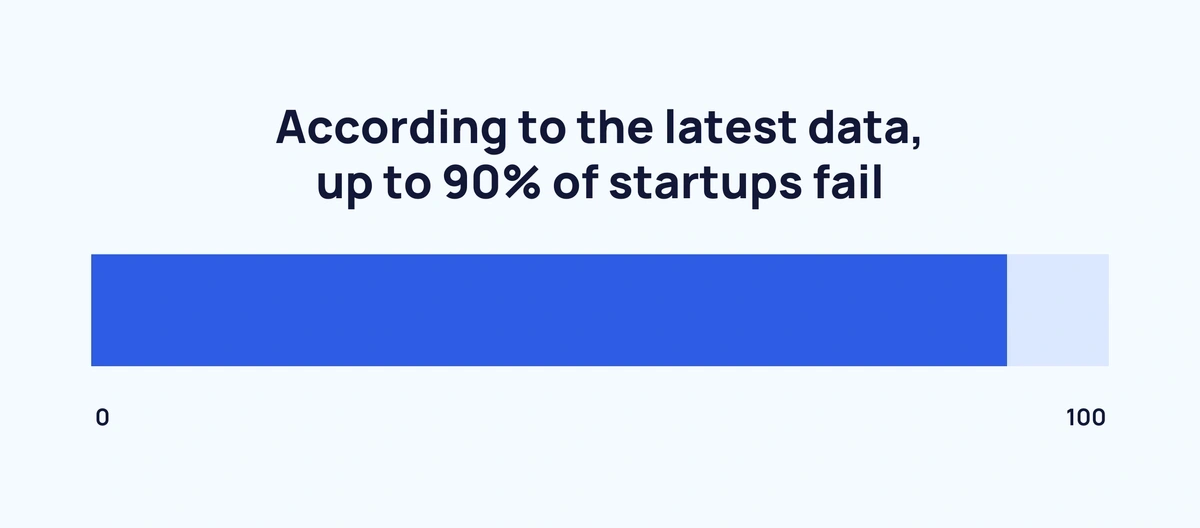
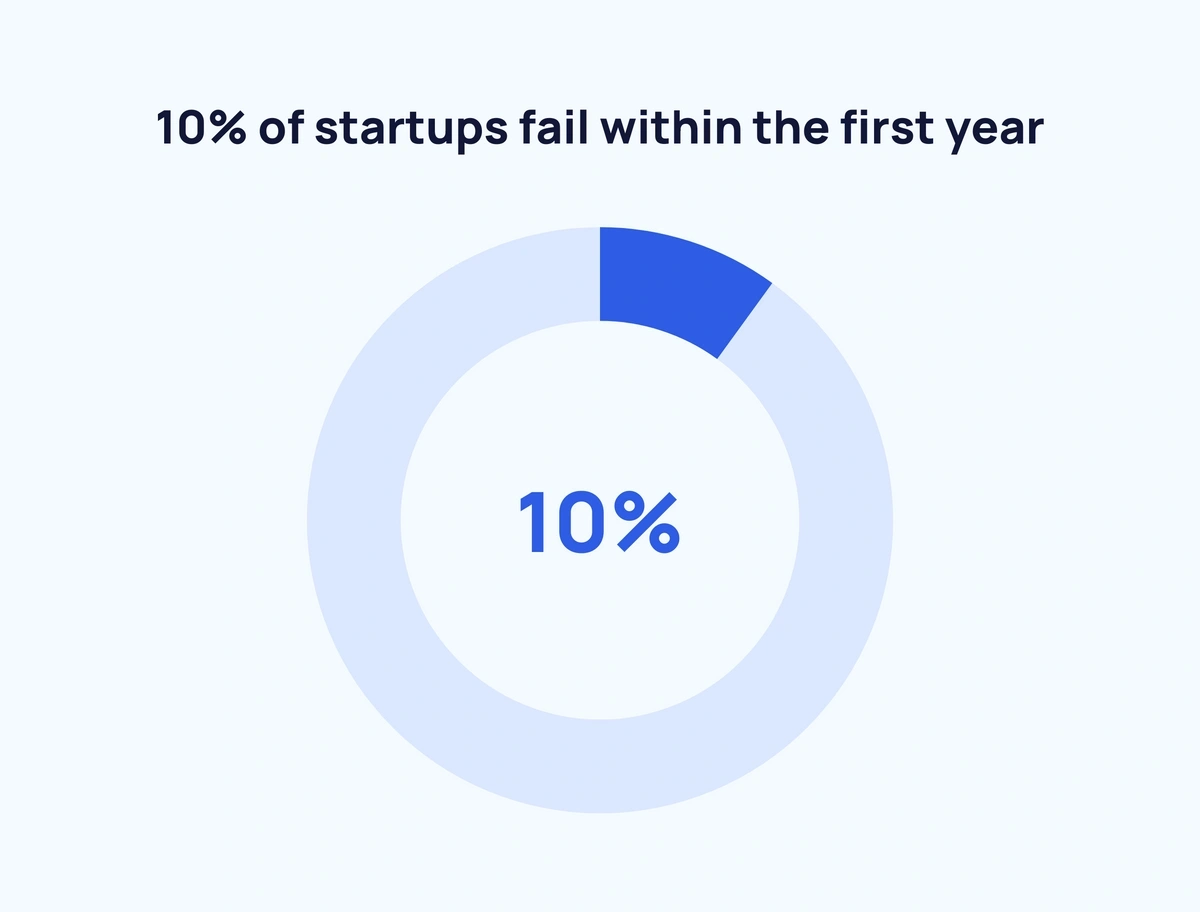
According to the latest data, up to 90% of startups fail. Across almost all industries, the average failure rate for year one is 10%. However, in years two through five, a staggering 70% of new businesses will fail.
This trend has been fairly consistent in the past 5 years, and there's no indication that it will change in 2025 or beyond.
How likely is your startup to fail? In this report, we take an in-depth look at what percentage of startups fail, why they fail, and vital statistics relating to startup costs, funding, and industry-specific data.
Startup Failure Statistics – Editor’s Choice
- The failure rate for new startups is currently 90%.
- 10% of new businesses don’t survive the first year.
- First-time startup founders have a success rate of 18%.
- The average cost of launching a startup is $3,000.
- Investors predict similar failure rates for AI startups
- Payroll is one of the highest costs a business incurs.
- 34% of small businesses that fail lack the proper product-market fit.
- 22% of startups that fail don’t have a sound marketing strategy.
- The average venture capital firm receives more than 1,000 proposals per year.
- Approximately 30% of startups with venture backing end up failing.
- Around 75% of all fintech startups crash within two decades.
- Startups in the technology industry have the highest failure rate in the United States.
Startup Failure Rate Statistics and Trends
Startup Failure Rates: How Many Businesses Fail in the First Year?
Approximately 10% of startups fail within the first year. According to the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics, the startup failure rate increases over time, and the most significant percentage of businesses that fail are younger than 10 years.
Over the long run, 90% of startups fail. In other words, only one in 10 traditional businesses in the startup category ultimately survive.
Business failure rates have remained more or less consistent since the 1990s across most industries.
Knowing what percentage of businesses fail and why they fail can help startup owners manage risks and ensure that their new business succeeds.
Industry data on startups from the Bureau of Labor Statistics provide valuable insights into the failure of startups.
Key Statistics
- 20% of new businesses fail within the first two years.
- 45% of new business startups don’t survive the fifth year.
- 65% of new startups fail during the first ten years.
- 75% of American startups go out of business during the first 15 years.
According to a VC investor, 85% of AI startups are doomed to fail in the first 3 years.
This failure rate is similar to traditional startups, indicating that AI is not without its challenges despite its benefits for new businesses.
That said, AI is still a new technology. The trend for AI startup success rates will only become clearer as more companies launch.
With AI coding tools like Cursor, Windsurf, and Lovable peaking in search interest in 2025, we can expect a lot of new startup activity in the immediate future.
Startup Success Rates
Generally, new business success rates are around 10% to 20% over the long term. However, many factors determine potential startup success.
The vast majority of owners who run successful startups claim to have relevant qualifications and experience in running their own businesses, according to Small Business Trends.
Another contributing factor to businesses’ long-term success is the owners’ ability to meet the needs of potential customers and implement proper risk management into their small business administration.
Below are notable small business success rate statistics.
Key Statistics
- First-time small business owners have a success rate of 18%.
- Business owners who failed in the past have a slightly higher startup success rate of 20%.
- Business owners who started a successful startup in the past have a business success rate of around 30% when starting a new venture.
Sources: Embroker, Review 42, US Bureau of Labor Statistics, Small Business Trends, SSRN
Build a winning strategy
Get a complete view of your competitors to anticipate trends and lead your market
Startup Costs Statistics
What Does It Cost a New Business Owner to Start Their Own Business?
According to the United States Small Business Administration, starting a small business costs, on average, $3,000. The average startup costs of home-based startups, including franchises, range from $2,000 to $5,000. Permanent business closures are often the direct result of the startup’s inability to meet expenses.
This section discusses significant startup costs statistics for new businesses.
Key Statistics
- Startups in online retail, accounting, landscaping, and construction typically have startup costs of up to $5,000.
- Healthcare providers, restaurants, and manufacturing companies are among the most expensive startup companies and usually require more than $100,000 to launch.
- A startup’s equipment costs can be as high as $125,000, depending on the industry and the startup’s product and service offers.
- The lowest average equipment costs for startups are $10,000.
- Payroll is among the most significant startup costs, with $300,500 being the average per five employees in the United States.
- 58% of small businesses in the United States start with less than $25,000.
- Startups in the venture capital industry, such as Uber and Airbnb, require debt of over $1 billion to be successful.
- Healthcare costs are among the most significant challenges new businesses face.
Monthly costs vary widely depending on the business’s location. For example, New York City is one of the most expensive locations for startups, with office space costing an average of $68 per square foot per month.
At $16 per square foot per month, Detroit’s office space is the most affordable. However, Detroit is one of the cities with the most expensive internet service (at a monthly average cost of $140.)
According to data from the World Bank, the cost of business startup procedures as a percentage of Gross National Income (GNI) per capita has declined steadily during the two decades. In 2019, this value for the United States was 1%.
Sources: SmartAsset, Pitchbook, Nerdwallet, Small Business Trends, The World Bank, Embroker, Findstack
Why Do Most Startups Fail?
Top Reasons Startups Fail
Why do startups fail? The relatively high startup failure rates are due to various reasons, with the most significant being the absence of a product-market fit, poor marketing strategy formulation and implementation, and cash flow problems.
Why do entrepreneurs fail? In most cases, a business fails due to multiple reasons.
For example, suppose the startup owner fails to draw up a comprehensive business plan or build a business model that seems sustainable over the long run. In that case, the startup might lose money, encounter operational issues, and run into legal problems.
AI startups face a different kind of challenge. It's easy to get overexcited with the speed with which AI solutions can perform important tasks for startups.
But this promise can also lead startups to scale faster than they can realistically manage.
Insufficient marketing is another major reason for the high business failure rates. A sound marketing strategy allows startups to strategically share offers with a target audience and present their products and services as a solution to prospective customers’ problems.
However, if no market exists for the startup’s product or service, even the most creative and well-executed marketing strategy will fail. Extensive market research is crucial to ensure that there is a product-market fit.
Want to Spy on Your Competition?
Explore competitors’ website traffic stats, discover growth points, and expand your market share.
Successful startups also encounter issues with product-market fit. However, the startup teams in these businesses do extensive market research, and they incorporate effective marketing strategies while adhering to a marketing budget.
Cash flow problems contribute significantly to the business failure rate in the United States. Most entrepreneurs who launch with insufficient funding, product or service prices that are not market-related, or optimistic sales projections end up with a failing startup.
In some cases, a startup fails because the founders don’t have the necessary qualifications or experience. Ideally, entrepreneurs should be industry experts with sufficient business experience.
What are the most common reasons for failed startups? The statistics below provide some insight into the top reasons startups fail.
Key Statistics
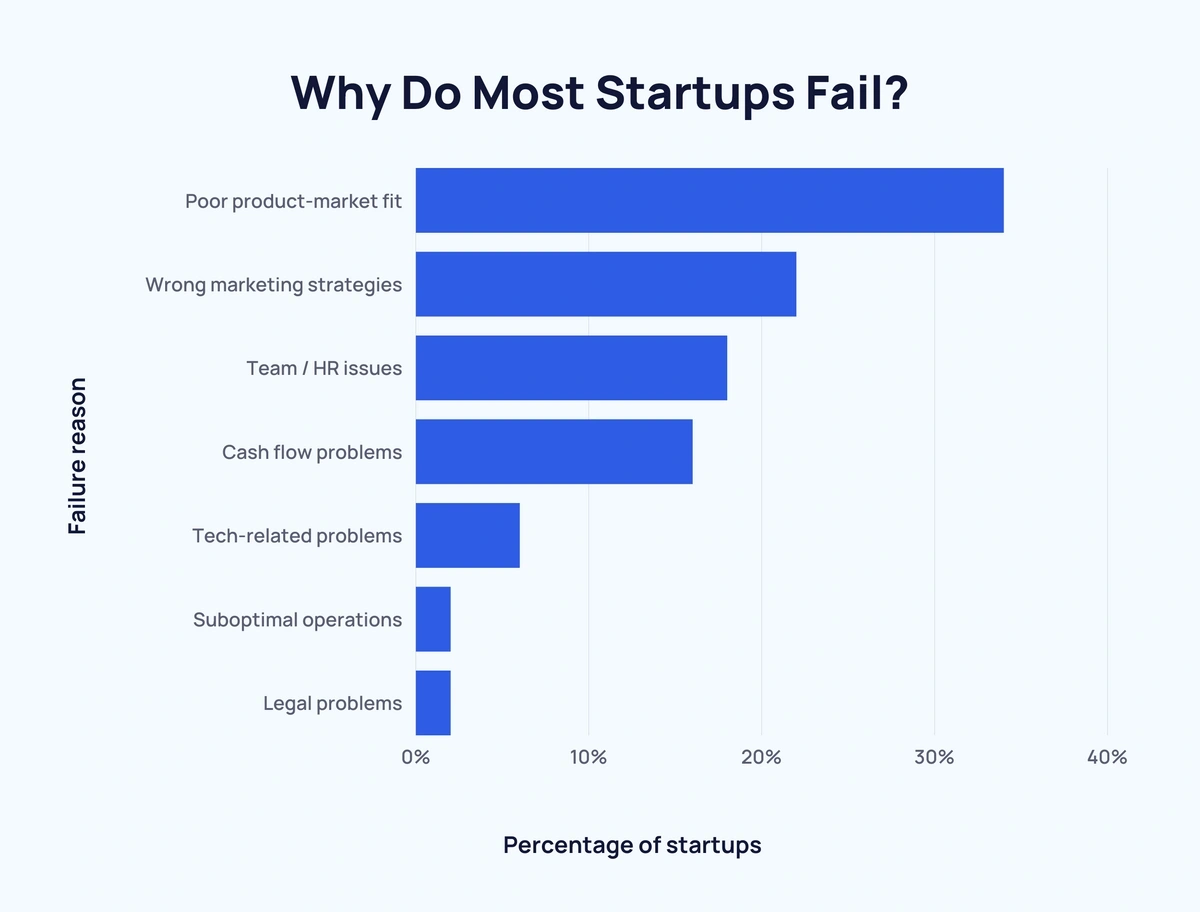
- 34% of startup failures are due to a poor product-market fit.
- 22% of failed businesses didn’t implement the correct marketing strategies.
- 18% of startups fail due to team problems and other human-resource-related issues.
- 16% of failures in the startup world are the result of cash flow problems and other financial issues.
- 6% of startup failures are due to tech-related problems, including poor cyber security and outdated solutions.
- 2% of startups fail due to sub-optimal operations.
- 2% of startups fail due to legal problems, such as issues with licensing, registering an unsuitable entity structure, and failing to formulate a partnership agreement that protects the interests of each co-founder.
Sources: Failory, Business News Daily, Investopedia, CB Insights, Review 42
Startup Funding + Investor Facts
Startup Failure Rate by Stage / What Percentage of Venture-Backed Startups Fail
What percentage of venture-backed startups fail? Generally speaking, for every ten venture-backed startups, around three companies fail, four businesses manage to repay the investment amount, and one business survives while generating sustainable returns.
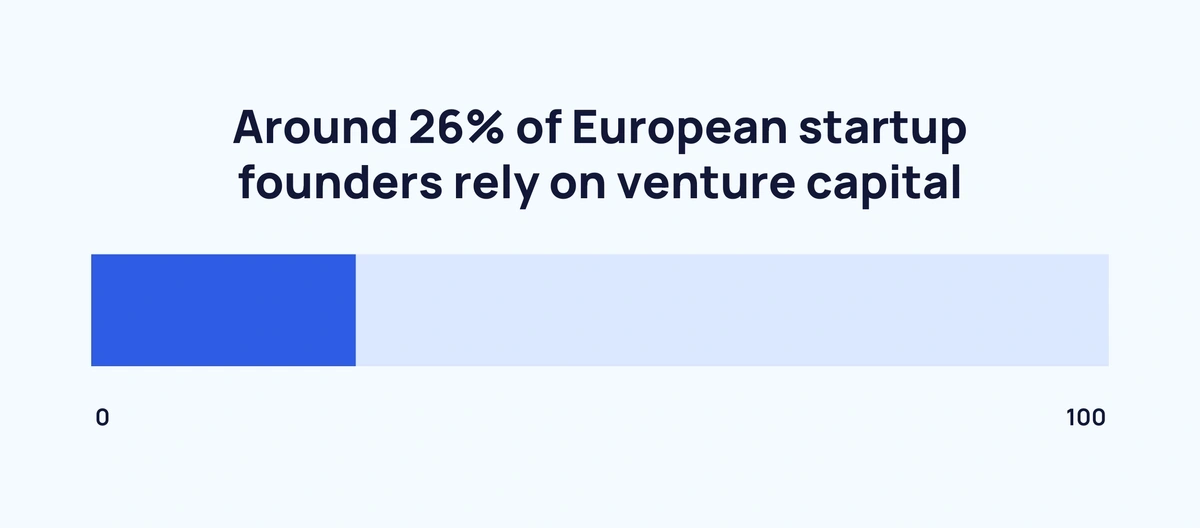
According to Forbes, less than 1% of small businesses in the United States receive funding from venture capital (VC) firms to cover costs. On the other hand, around 26% of European startup founders rely on VC funding.
What percentage of venture capital investments fail? Below are statistics relating to venture-backed companies.
Key Statistics
- On average, a single VC firm receives more than 1,000 proposals per year.
- Around 25% of new businesses don’t receive all of the funding required to launch, thus restricting their sustainable growth.
- On average, credit card debt, business loans, and lines of credit amount to 75% of new business financing.
- Around 30% of all venture-backed startups fail.
Sources: Scale Finance, Statista, Forbes, Money Crashers, National Small Business Association, Fundera
For Idea-stage Startups:
Generally, the startup failure rate by stage decreases with every round of funding. The Startup Genome Project found the following about idea-stage startups:
- Early-stage startups need to spend up to 3x longer validating their target markets than their founders anticipate. One of the aims of the more extended market validation period is to prevent cash flow issues from running the project into the ground before the startup has the chance to determine the market-product fit.
- Startup founders tend to overestimate the company’s intellectual property by up to 255%.
- Early-stage startups can increase user growth by up to 3.6x and generate 2.5x more returns by pivoting once or twice. Startups that don’t pivot or pivot more than two times tend not to perform optimally.
During the idea stage, the primary objective should be to establish a product-market fit. Using the lean startup methodology, business owners need to optimally validate the market using time and resources, giving themselves sufficient leeway to pivot.
Sources: The Lean Startup Methodology, Startup Genome
For Later-stage Startups:
According to the Startup Genome Project, the four startup stages include:
- Discovery
- Validation
- Efficiency
- Scale
Later-stage startups that scale prematurely are inconsistent and more likely to fail. Premature scaling involves investing too many resources during the first stages of the startup journey, increasing the failure rate.
According to the statistics of the Startup Genome Project, inconsistent later-stage startups scale prematurely by doing the following:
- Generating three times more capital during the efficiency stage and 18 times less capital during the scale stage.
- Self-reporting valuations of $10 million before they reach the scale phase. On the other hand, consistent startups report valuations of around $800,000.
- Onboarding 75% more paid users during the first two phases. For the sake of comparison, consistent startups have 50% more paid users during the scale stage.
- Writing around 3.5 times more code during the discovery stage and writing 2.25 times more code during the efficiency stage.
Sources: Startup Genome, Failory
Failure Rate Implications for Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurship failure costs that business owners incur can be financial, emotional, and psychological. Starting a new business that ends up failing can also cost entrepreneurs valuable time that they could have used to build a lucrative career or another source of income.
Small business trends relating to startup failure rates are bleak and often discourage would-be entrepreneurs from launching new ventures. When considering how many entrepreneurs fail, launching a startup doesn’t appear to be a financially viable option for anyone.
However, the goal of failure statistics is not to discourage budding entrepreneurs. Instead, these figures aim to help small businesses mitigate their risks and build the one in ten businesses that survive and achieve growth over the long run.
Launching a new startup is not a gamble but a calculated risk that startup owners can manage successfully. Various concrete reasons exist for the high failure rate among new businesses.
Startup founders need to understand the reasons that startups fail and implement all necessary measures to avoid the pitfalls that most businesses encounter.
Source: Failory
Failure Rate Implications for Startup Investors
When considering how many startups go out of business, one might wonder how startup investors can be profitable. In short, investors attempt to conduct their investment in a manner that allows successful startups to offset the losses of the startups that fail.
Startup investors are generally up to date on how many new businesses succeed and how many fail. Venture capital investor failure costs can be high, especially in the case of sizable investments.
Consequently, these investors go to great lengths to ensure that they minimize their investments in potentially unsuccessful companies. Before investing, an investment firm will typically scrutinize the startup’s business plan to determine its potential return on investment.
Investors consider various factors before giving startups money in exchange for ownership:
- The startup’s past financial performance
- The size and validity of the startup’s target market
- All data-based financial projections
- All sales channels and their effectiveness in reaching the target audience
- Existing and potential future competitors in the market
- The projected timeline for generating returns
- Potential pitfalls and the owner’s modus operandi for addressing them
Investors will typically only invest in businesses with a unique idea and clear-cut investment structure.
Source: Failory
Startup Failure Rate by Industry and Sector
Statistics for Fintech Startups
Financial technology (fintech) startups combine technology and innovation to deliver conventional financial solutions. Successful fintech startups tend to base their operations on continuous user testing and information-based iteration. These startups support organizations in banking, accounting, and other relevant industries.
The national percentage of fintech businesses that fail is relatively low compared to the startup crash rates in other industries, including startups in Silicon Valley.
Key Fintech Startup Statistics
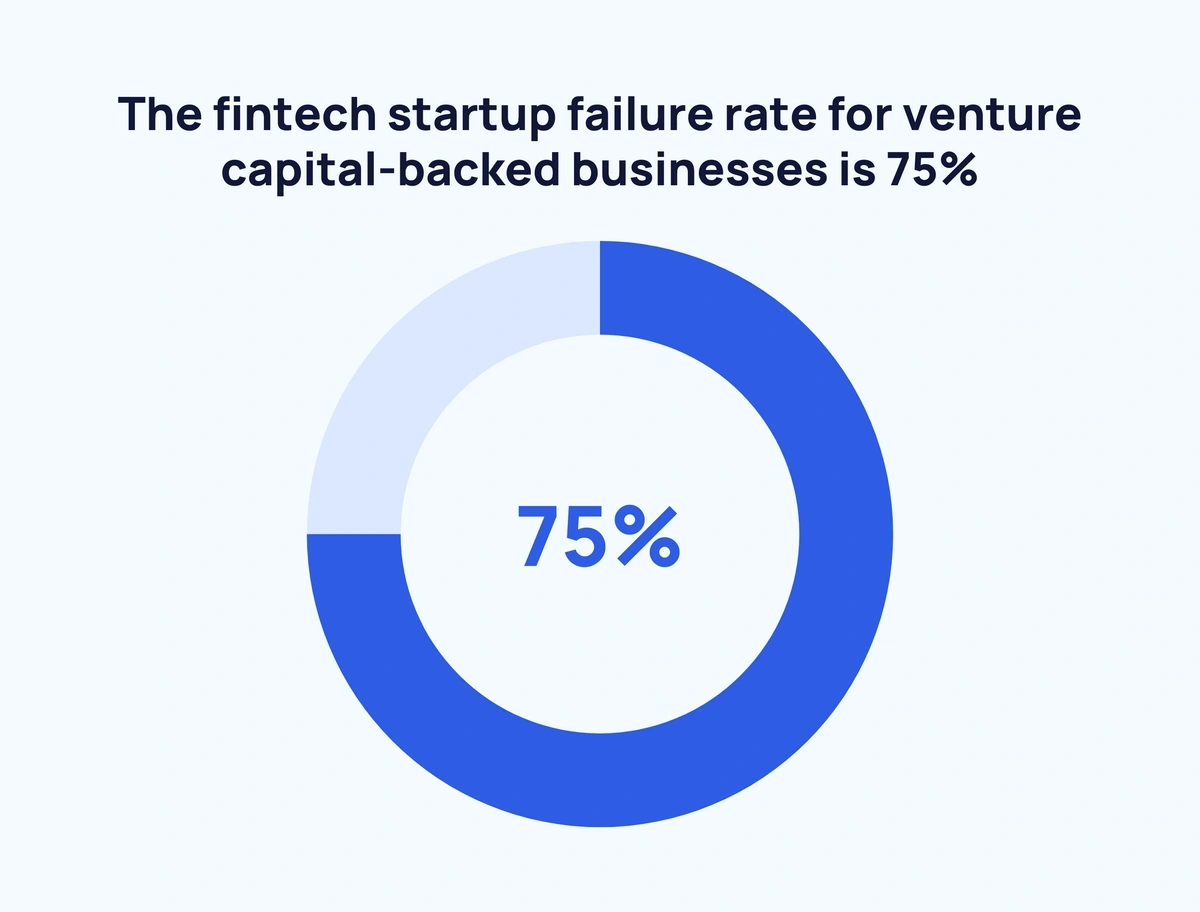
- The fintech startup failure rate for venture capital-backed businesses is 75%.
- Global fintech investments by venture capital firms increased from $1.8 billion in 2011 to $30.8 billion in 2018.
- Currently, the fintech industry receives $50 billion in investments per year.
- Approximately 80% of all financial institutions in the United States are partners with fintech service providers.
- Currently, there are more than 8,775 fintech startups in the United States.
- At a value of $131 billion, the Ant Group is the largest fintech company globally.
- The global fintech industry was valued at $310 billion in 2022.
Sources: The Fintech Mag, McKinsey & Company Report, Balancing Everything
Statistics for Technology Startups
Some of the best-known tech companies include Google, Facebook, and Apple - all of which were startups at some point.
The profitability and profile of these tech giants attract large numbers of entrants to the market. However, the tech industry has multiple pitfalls, and the tech startup failure rate is significantly higher than the crash rate of other industries.
Tech Startup Statistics
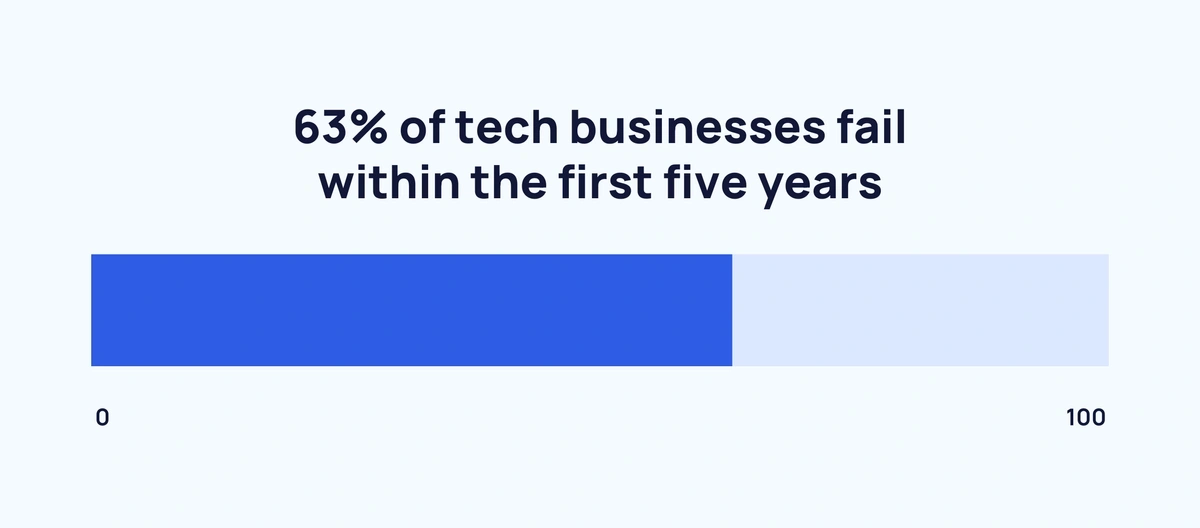
- At 63%, the percentage of tech businesses that fail within the first five years is relatively high.
- Every year in the United States, 20 tech companies launch that will go on to generate $100 million in revenues.
- The average age of a tech startup founder in the United States is 39.
- At a value of $1.6 trillion, the United States has the most significant technology market in the world.
- Tech companies pay employees an average of $102,000 per year — more than double the United States average.
Sources: Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation, Forbes, Embroker
Statistics for Real Estate Startups
The real estate sector is among the most significant industries in the world. In the United States, real estate transactions contribute significantly to the GDP, and the industry is one of the most attractive for startups.
Real estate startups include businesses providing conventional real estate services and proptech (property technology) startups. As with the tech industry, the real estate startup failure rate is relatively high.
Real Estate Startup Statistics
- The percentage of real estate businesses that fail within four years is 48%.
- Real estate startups in the United States generated $1.9 billion during 2019.
- Residential real estate startups that incorporate artificial intelligence into their offers attract the most investments.
- Office-sharing startups attract the most VC funds of all real estate startups. Industrious is one example of an office-sharing startup, and it generated $62 million in revenues during 2017.
- Approximately 31% of United States-based commercial investors consider investing in proptech companies.
Sources: Embroker, Tech, HousingWire, Crunchbase
Statistics for Construction Startups
Construction startups increasingly see success as industry leaders. These businesses create and deliver innovative solutions to save construction time and costs while enhancing build quality and ensuring compliance with relevant standards.
Despite the high demand for revolutionary construction solutions, the construction startup failure rate is one of the highest in North America.
Construction Startup Statistics
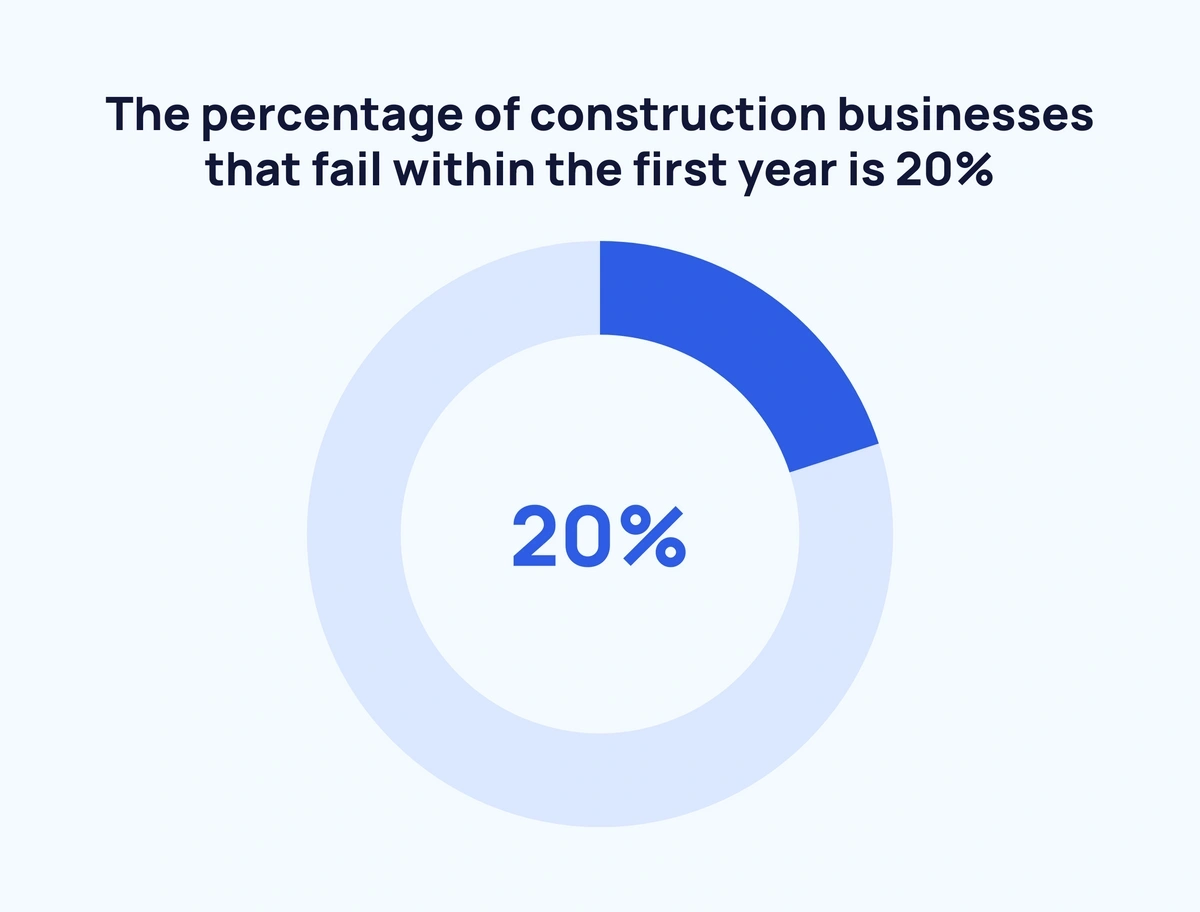
- The percentage of construction businesses that fail within the first year is 20%.
- Two out of three construction startups go out of business within the first ten years.
- Statistically, a construction startup only has a 36.6% chance of surviving longer than five years.
- In 2017, startup investors contributed to 87 deals in North America, double the amount of deals in 2013.
- The residential housing sector is the fastest-growing sector in the construction industry.
- According to estimates, artificial intelligence technologies will increase profits in the construction industry by up to 71%.
Sources: Pit & Quarry, Crunchbase, Small Business Trends
Conclusion: Future of Startups
Despite being in an entrepreneurial country, only one in ten startups in the United States survive and achieve fast growth over the long haul. This statistic is shocking and can be highly discouraging to prospective entrepreneurs.
However, these statistics provide valuable insights into potential pitfalls. With due diligence and proper risk management, startups have a bright future.
If you enjoyed these statistics, have a look at our top 11 startup trends and our 8 entrepreneurship trends you need to know.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more